What Is A Ruptured Aneurysm And How To Prevent It?
The aneurysm can be of congenital origin or it can accompany other pathologies. At first, it often appears asymptomatically, but then it develops into eye pain, causes brittleness and dilated pupils.
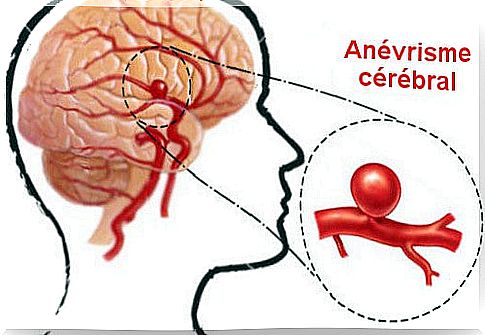
Aneurysm rupture. You may have heard of it before. Even you or one of your relatives has already suffered from it. These are small blood vessels which, following a strong blood flow, dilate in our brain and exert dangerous pressure.
It is in fact a sensitive subject that must be taken into account since the percentage of risk has a direct relationship with our lifestyle. Do you want to know more about this phenomenon? Read on.
1. What is a ruptured aneurysm?
His name may scare us. But don’t panic, most of the time, this problem is solved with an intervention. The most important thing is to know the subject, to be able to identify the symptoms and to try to have the healthiest life possible.
Now let’s get right to the point: a brain aneurysm happens when a blood vessel fills with blood in our brain and puts pressure on it.
Normally, they occur in the lower part of the brain: this is important to know. If they are not taken care of in time, it can lead to serious problems. The risks are: either the pressure causes irreversible pain or the blood vessel starts to bleed.
2. What are the causes of a brain aneurysm?
Are there really ways to avoid it? The answer is yes and no”. Most of the time, it is a congenital disease, meaning that this small blood vessel was already swollen in our brain from birth.
The other probability is that we suffer from an aneurysm due to another disease, such as problems with the kidneys, circulatory, veins or arteries …
Infections, high blood pressure, having suffered a blow to the head, having any cancer… All of this can also cause these small dangerous accumulations of blood in our brain, and affect the proper functioning of the blood flow.
3. Who is most at risk for a ruptured aneurysm?

The adult population in general, and people between the ages of 30 and 60 in particular. It should also be pointed out that, according to statistics, women have a higher risk of suffering from an aneurysm.
These swollen blood vessels are considered serious once they reach a diameter of 15mm in our brain since they can start to bleed and thus put more pressure on our brain.
The real risks then appear. When they burst and bleed inside the brain, a stroke occurs. It is a ruptured aneurysm, which is often the cause of other aneurysms.
4. What are the symptoms?
Unfortunately, many brain aneurysms don’t show symptoms until they are very large or flare up. If they are small, that is, they are less than 10 mm, they do not show any discomfort.
But if they are bigger and they grow even bigger, then you will start to feel their effects.
How do we know we have an aneurysm that may be about to burst? We mostly feel pain above and behind the eyes, brittleness or paralysis on one side of the face, and we have dilated pupils.
You should also consider the symptoms associated with an aneurysm that has started to bleed. Sudden and intense headache, we get up in the morning seeing double, with a heartache, vomiting, pain in the neck, fainting …
Other signs, for example, are a drooping eyelid, greater sensitivity to light, more difficulty concentrating, having seizures and the worst headache we have ever felt. These symptoms are so obvious that you should see a doctor immediately to confirm them.
5. How is a ruptured aneurysm diagnosed?
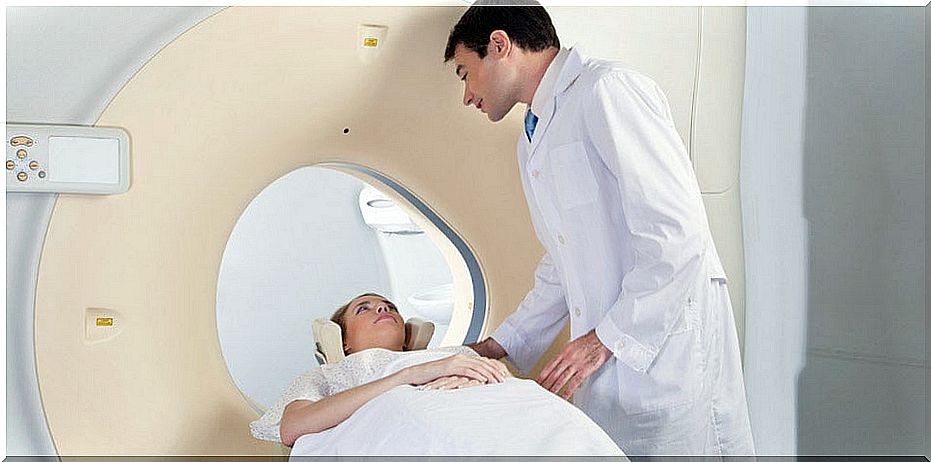
To check if we have an aneurysm, we need to do a CT scan or an MRI. Many aneurysms are detected by chance when patients are tested for other conditions.
6. How are brain aneurysms treated?
First of all, it should be emphasized that each patient is unique. Depending on his personal history and the size of his aneurysm, doctors will make an appropriate choice. In general, we opt for two techniques.
- The first is the microvascular prosthesis with which we succeed in stopping the blood flow of the aneurysm. The neurosurgeon accesses the blood vessel that supplies the aneurysm in the brain and inserts a small metal clip that looks like a staple into your neck.
- The other technique is not done in the brain but through endovascular embolization. The doctor inserts a catheter into the artery in the groin, and advances it to the aneurysm with a platinum wire. It blocks him and heals him.
Today, the techniques are very advanced, so do not be afraid. Most of the time, aneurysms resolve themselves with ease and success. You just have to be attentive to the symptoms.